Access the Elastic Beanstalk Environment
Under Services, access Elastic Beanstalk. Now in the Elastic Beanstalk dashboard, you would be able to see a pre-deployed environment under the All environments box.
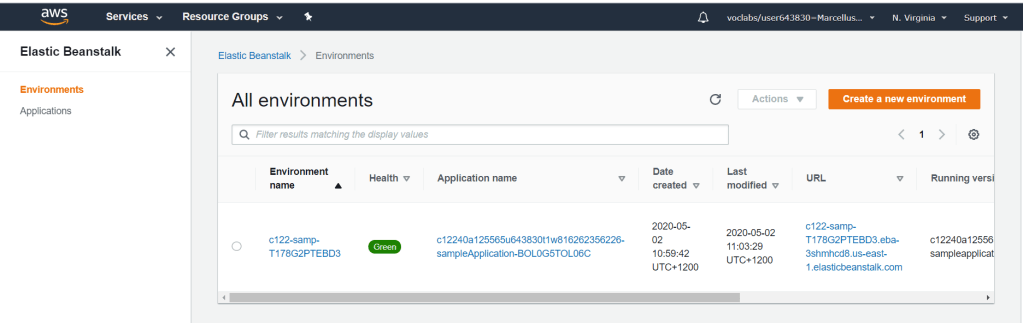
Click on the environment name to display it for more detailed view. Make sure that the environment health is green which means good. This environment is ready for codes to be deployed in.
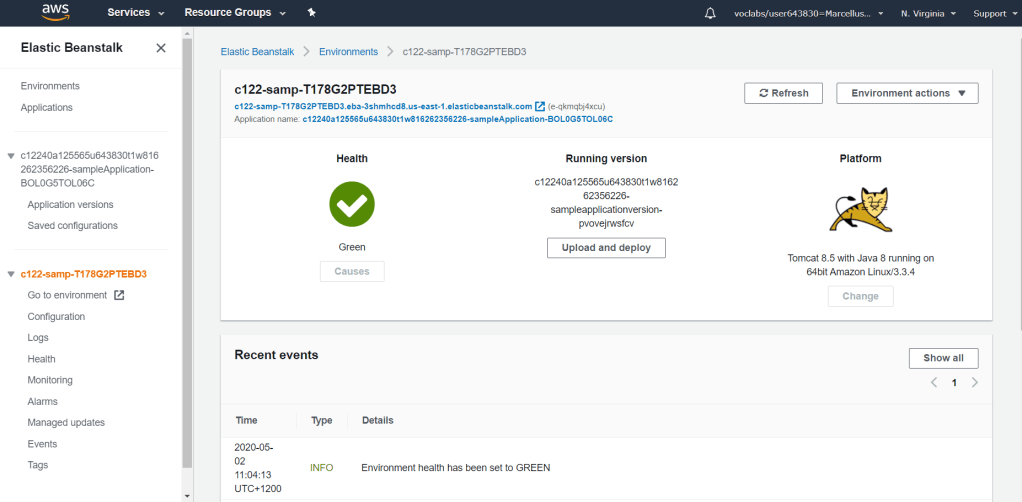
Click on the URL (ending with elasticbeanstalk.com) to access the running application in the environment. You should not be able to see anything as there is no code yet in the environment.
Deploy a Sample Application to Elastic Beanstalk
For the sample application, we will use Java Apache Tomcat. I already downloaded the zip file from https://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticbeanstalk/latest/dg/samples/java-tomcat-v3.zip.
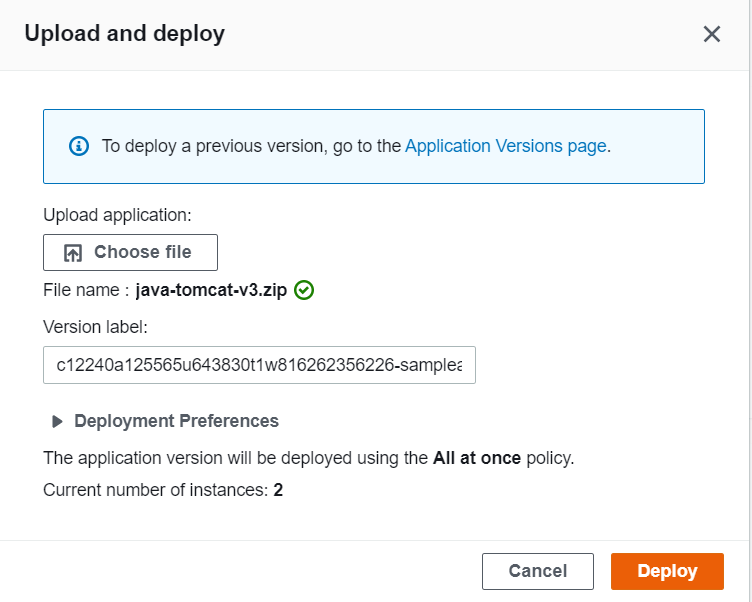
In the Elastic Beanstalk environment dashboard, click Upload and Deploy. Click Browse or Choose File and choose the sample application zip file that we have downloaded just now. Click on Deploy if done.
Now, if you access the Elastic Beanstalk URL again, you will should be able to access the application.
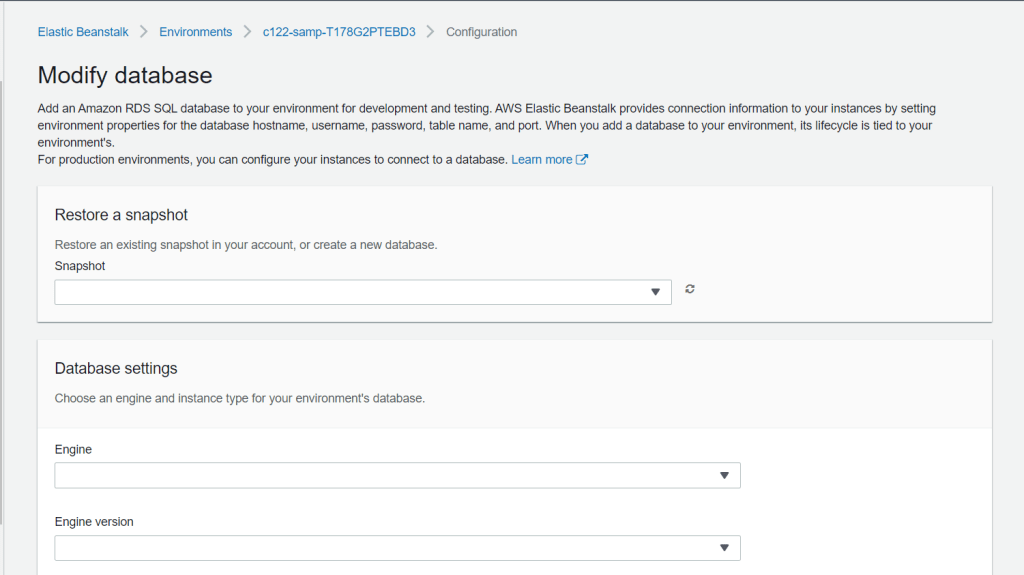
Still in the Elastic Beanstalk page, go to Configurations from the left pane. At the bottom of the page, you will find Database row. Click Edit. This configurations are responsible for assigning database in your environment. You can easily attach a deployed database into Elastic Beanstalk.
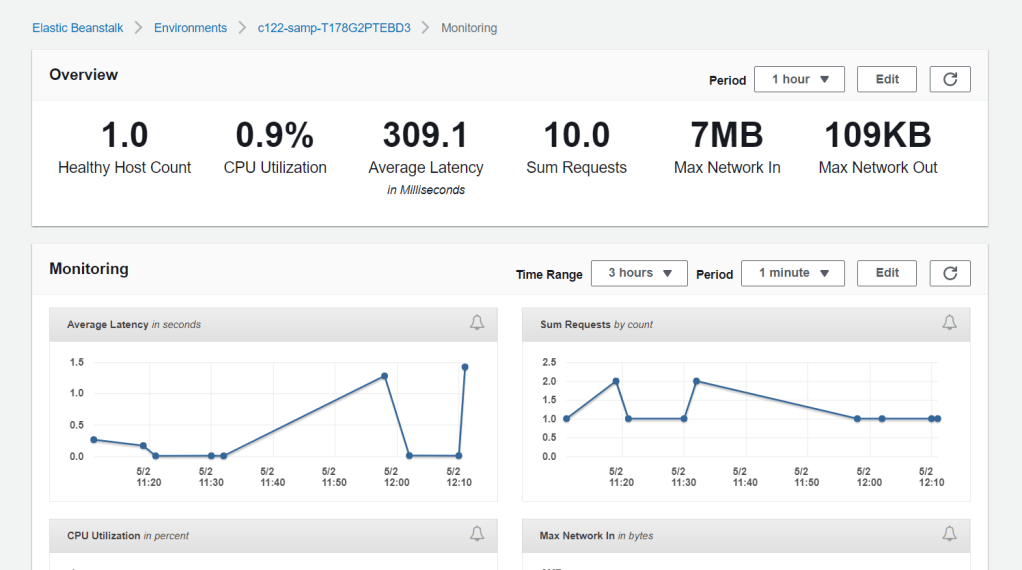
In the left pane, access Monitoring. You will be able to see all sorts of parameters regarding your environment status.
Explore AWS Resources to Support Elastic Beanstalk Applications
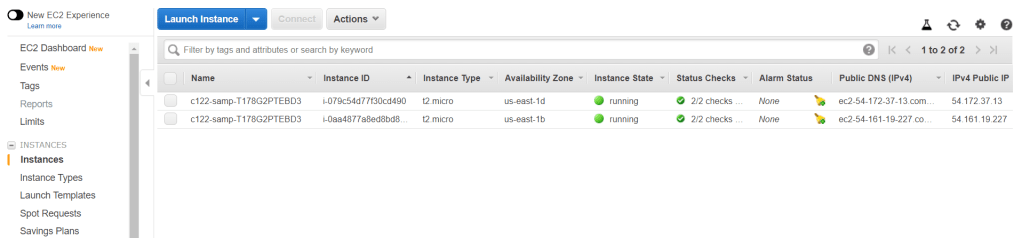
Go to EC2 dashboard and access Instances. In this lab, there are 2 instances that are already running. These are instances which are build by Elastic Beanstalk.
Critical Thinking
AWS Elastic Beanstalk is a powerful orchestration tool for deploying an application without worrying about the infrsatructuree pre-requisites. Other than that, you still have the ability to easily modify all the instances that are deployed.
Diving deeper into the capabilities of AWS Elastic Beanstalk, we will try to cover the details which supports the running application. From the EC2 security group, there are security groups dedicated for Elastic Beanstalk and for the Elastic Load Balancer which are created according to the application requirements. It has been configured for allowing inbound HTTP traffic.
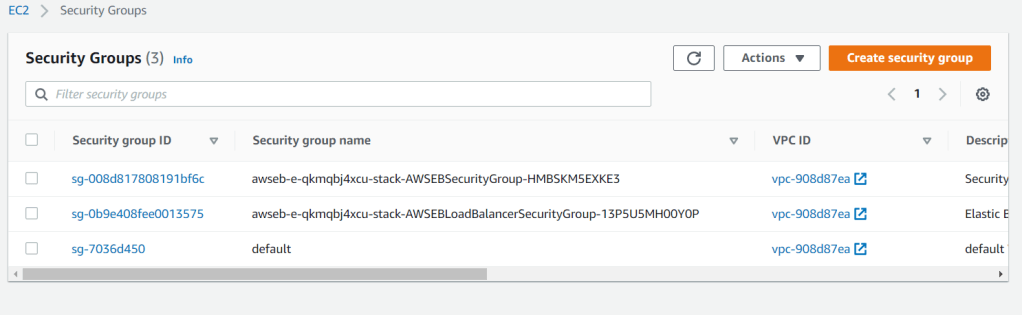
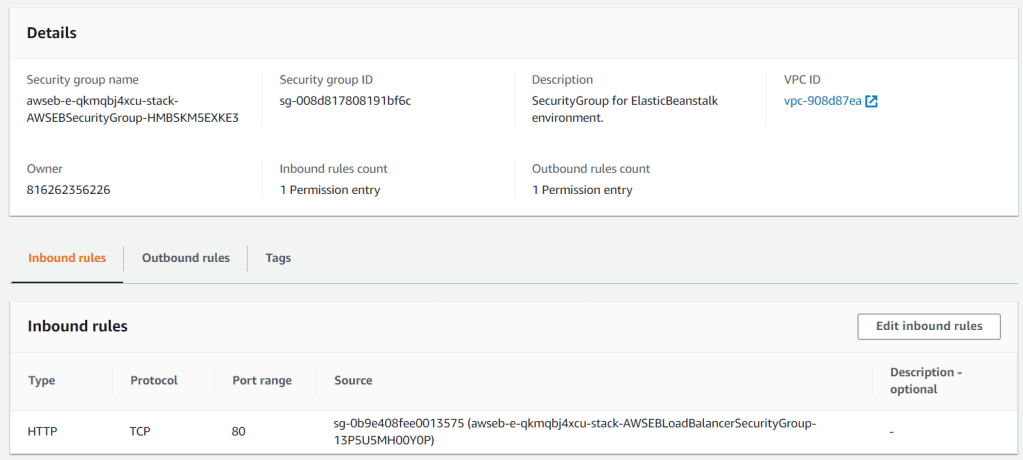
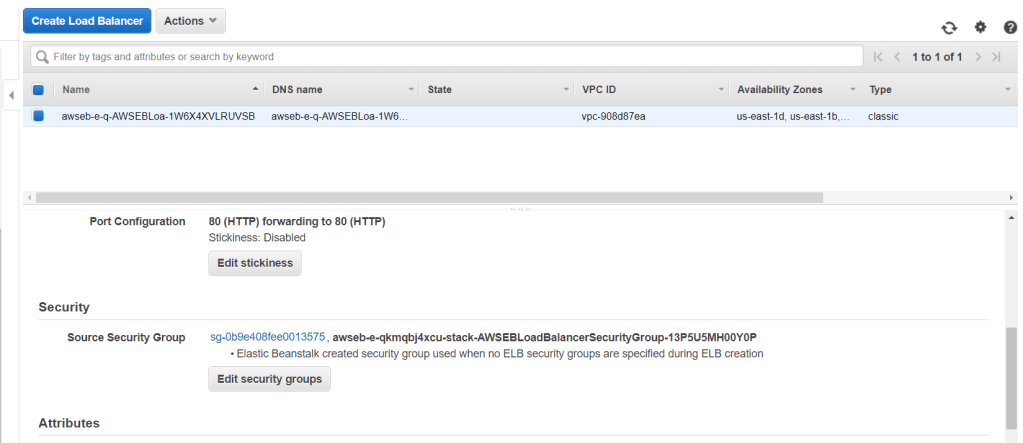
You can also see the Elastic Load Balancer created by Elastic Beanstalk with its own security group.
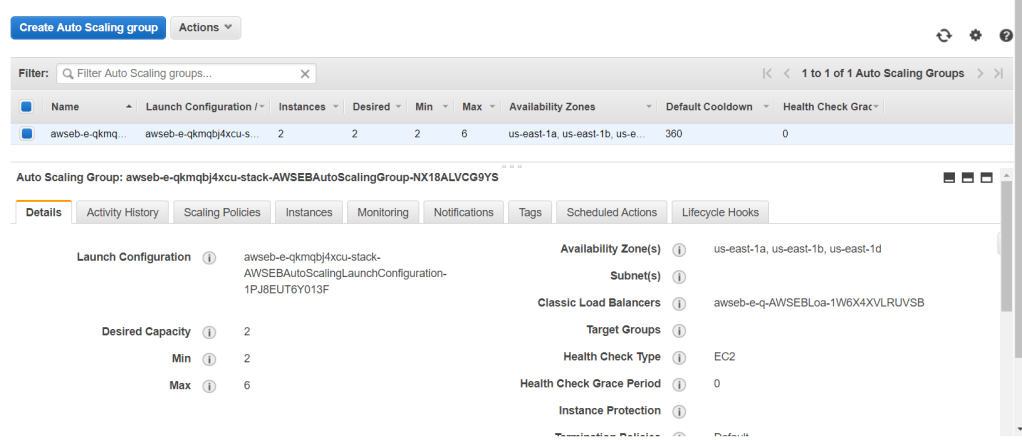
In addition to that, an auto scaling group is created by Elastic Beanstalk which consists the 2 EC2 instances as well.
From this lab, we can understand the versatility of AWS Elastic Beanstalk on deploying an application. Infrastructures are automatically deployed and set to the appropriate configurations. In addition to that, we can still have full access to modify all these resources as needed.
