Update on Smart Printers
To create a clear description and usage of smart printers, I will state the system in more details here. In addition to my previous explanation on this emerging technology, smart printers aim to create operational efficiency, improved service quality and sustainability.
Operational efficiency aim to create a monitoring system that provides accurate delivery of information and potential issues on the printer. This would increase the efficiency on fixes with less time spent to do routine check by service staff or engineer.
By understanding the usage level and pattern of a printer, a company could assess on how the services could be improved. This information would be used to improve some maintenance model of the business to match their requirements. As the needs of business will always fluctuate, this technology has the capability to assess the data well.
Environmental impact should also need to be considered these days. Automatic system that could detect patterns could implement an energy saving program on certain time which the printer are not used as much.
This smart printing device aims to create a cost and work efficient workflow for a business.
Reference: https://www.capitalmds.com/iot-smart-printing/
Business Report Workflow
The business report will describe a short explanation and implementation of smart printer on a company with COBIT 5 and ITIL. I will cover COBIT 5 and my teammate Sinhara will do ITIL. After the individual description on both frameworks, we will compare which concepts are the same and which are different. As what I understand so far, there would be many differences between both frameworks as it uses different approaches and covers different aspect of an IT service. With this in mind, we would explain more on what the framework covers which the other do not. Thus, the business report will result with a complimentary implementation of both COBIT 5 and ITIL framework together in a business concept.
After this post, I will try to find some references regarding existing COBIT 5 implementation. Afterwards, everything will be set for the business report to start.
Meanwhile, this post will continue to gather information about COBIT 5 principles.
Principle Three
With increasingly challenging task on managing and governing IT services with the addition of pressure from other organizational-related entity, COBIT 5 offers a single and integrated framework. There are 4 reasons why COBIT 5 serve as this, which are:
- COBIT 5 aligns with other latest relevant and frameworks which integrates all governance and management frameworks
- It provides a single and integrated guidances with non-techincal language
- Provides simple architecture for structuring guidance materials and producing a consistent product set, such as ISACA research, ISO, ITIL, etc.
- Integrates all best pratices over IT governance and management
Principle Four
To enable a holistic approach, COBIT 5 provides 7 enablers that will affect the outcome of the governance and management processes. These enablers include all internal and external resources as well as activities and responsibilities of IT and non-IT functions. These 7 enablers are shown in this figure below.
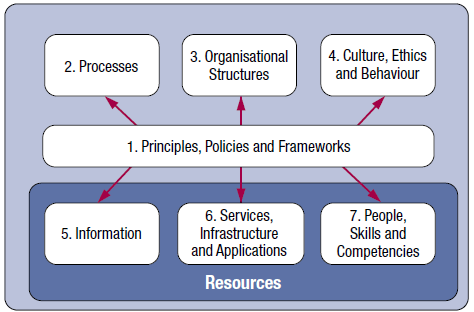
These enablers covers all enterprise resources to govern and manage. This enablers are interconnected by one another resulting each enablers would require other enablers’ input to be effective. Some enablers would also provide an output for other enablers to make it efficient. Below, I provide a detailed explanations on each enablers:
- Principle, Policies and Frameworks translates desired behaviour to practical guidance for day-to-day management
- Processes defines as a set of practices and activities to achieve certain objectives which produce a set of outputs that support the achievement of IT-related goals
- Organisational structures are key decision making entities in an enterprise
- Cultures, Ethics and Behaviour of individuals and enterprise should be taken more into account in governance and management activities
- Information covers throughout the organization and required to keep the organization running and well governed. At operational level, information is key product of the enterprise
- Services, infrastructure and Applications provide the enterprise information technology processing and services
- People, Skills and Competencies are the people required for successful completion of all activities, making correct decisions and taking corrective actions
To support the enablers, COBIT 5 provides Enabler Dimensions to support a common, simple and structured method for enablers. These dimensions also allows an entity to manage enablers’ complex interaction and facilitate successful outcomes from the enablers. These are COBIT 5 enabler dimensions and its performance management.
To define more in the enabler dimensions, below are more detailed information:
- Stakeholder – parties who play an active role in an enabler which include internal and external stakeholders
- Goals – achieved goals provide greater enablers value. These goals can be categorized to 3 which are intrinsic quality, contextual quality and accessibility and security
- Life Cycle – defines the life cycle of enablers from start to disposal. Life cycle applies to information, structures, processes and policies
- Good Practices – provides examples or suggestion on what is the best method to implement the enabler and which work products or inputs and outputs to support the achievement of the enabler goals
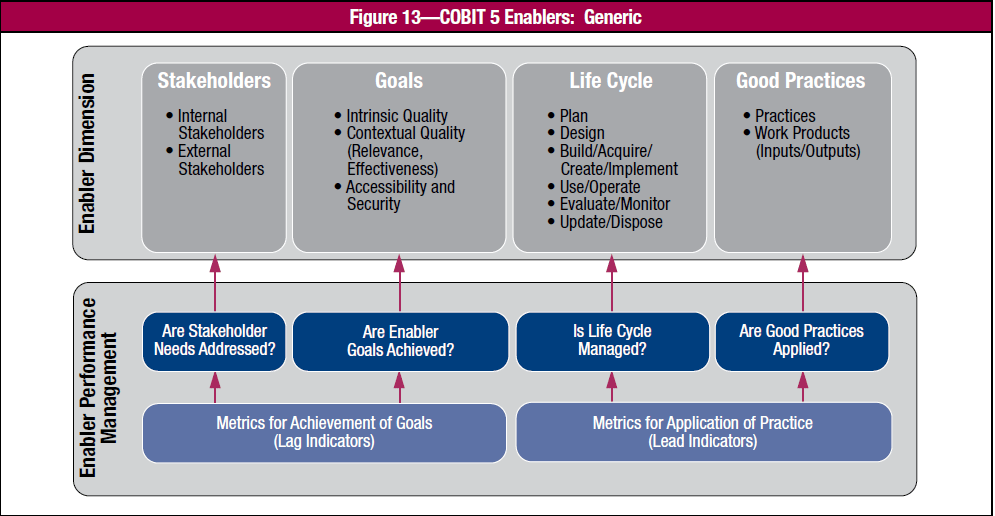
Enabler performance management helps direct the enablers’ outcome. Through the 4 question stated, it provides metrics to support these enabler dimensions. Lag indicators will affect enablers outcome and measure to what extent the goals are achieved. Lead indicators controls the functions of the enablers itself.
Principle Five
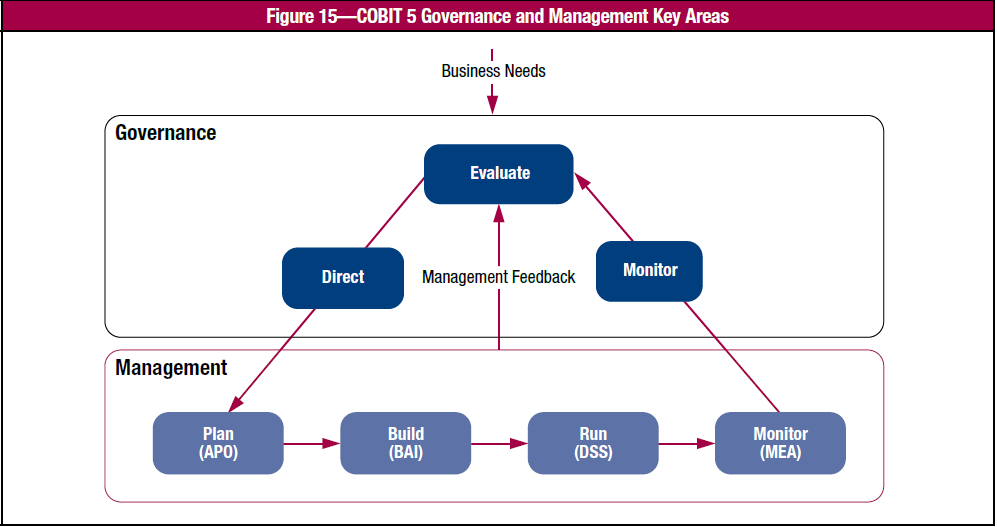
COBIT 5 emphasize on separating governance from management. The key areas that governance covers:
- Evaluate – Identify and agree on objectives that must be achieved
- Direct – Through prioritisation and decision making
- Monitor – Performance and compliacne against objectives
And the key areas for managements are:
- Plan
- Build
- Run
- Monitor
The key areas for managements ensure all activities undertaken and monitored as directed from governance function.
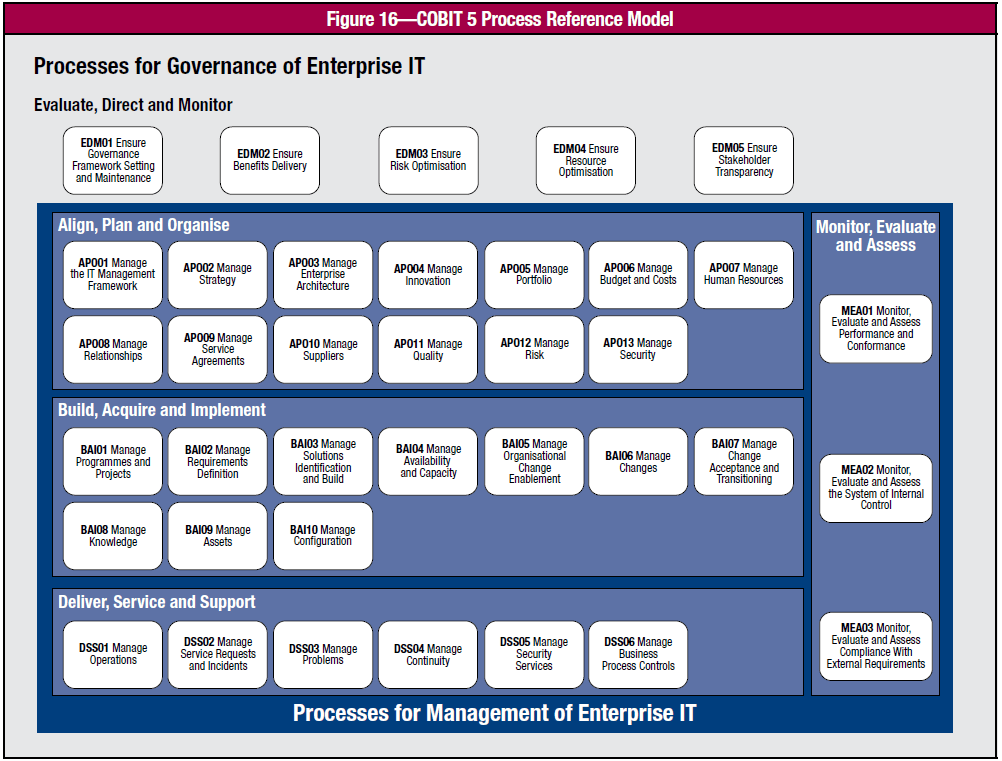
COBIT 5 provides a process reference model which includes governance and management processes. As different enterprises have different resources and objectives, these processes could be adjusted as they see fit as long as it aims to achieve the governance and management goals.
